Essential Steps and Key Skills to Become a Successful Future Finance Professional
Essential Steps and Key Skills to Become a Successful Future Finance Professional
Steps to Become a Future Finance Professional – Key Skills and Career Path
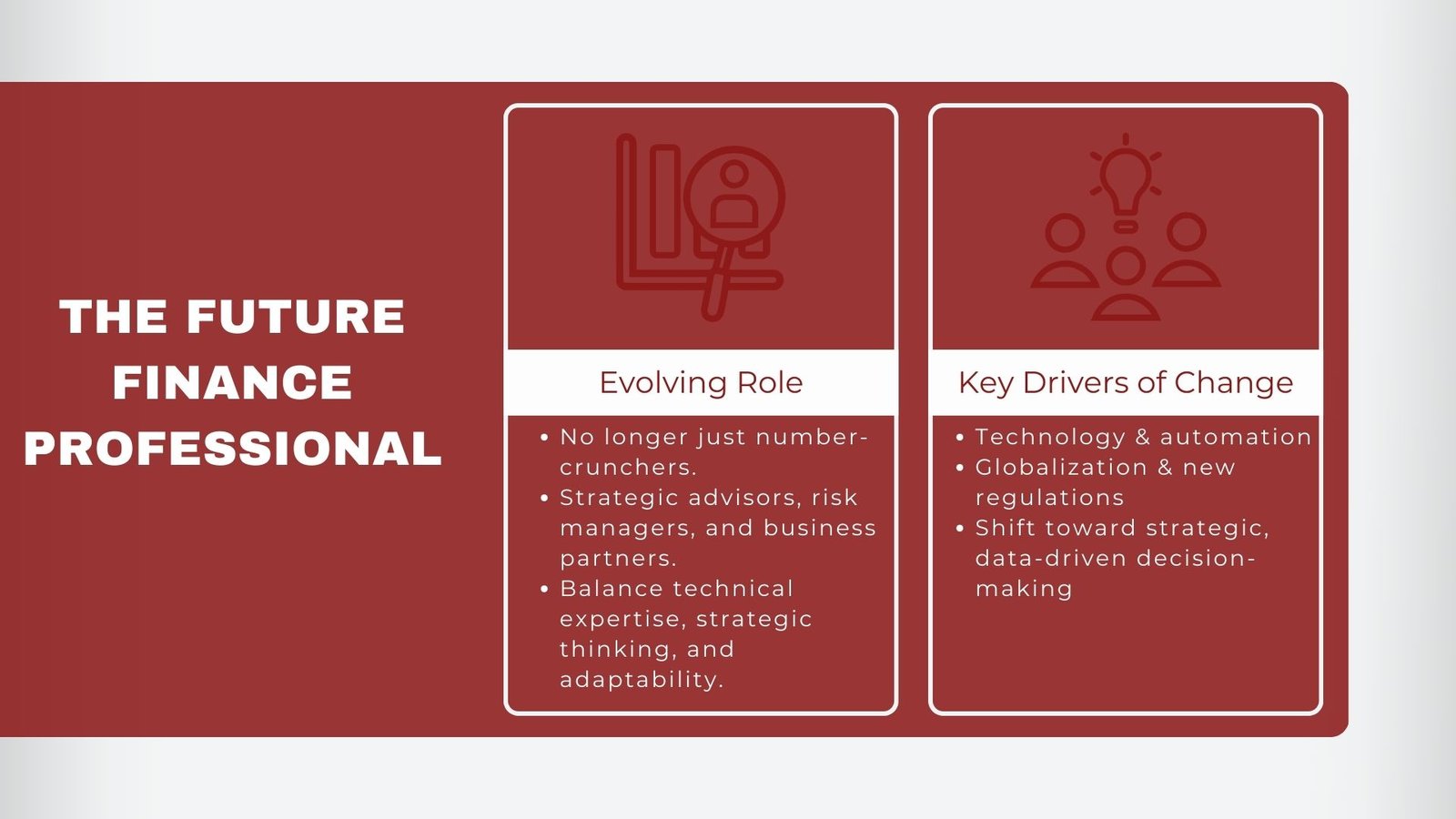
Changes in technology, rules and regulations, globalization and altered company priorities, are transforming the finance profession at a rapid pace. The future financial professional need not necessarily be a number cruncher, but is required to have a solid technical skill base along with the high-level intuition and business understanding and the flexibility to go with a complicated state of market conditions.
It is not merely an evolution in attempting to keep up with technological tools and learning to use spreadsheets, it is a new definition of how finance can enter into the growth potential of the business and in decision making as well as risk management. The path to success is an intentional combination of analytical capabilities, leadership skills, and future-proof skills that those, who want to succeed in their profession, need to take.
In the historical context, the role of the finance was more in terms of reporting history and compliance so that all the undertaken transactions were recorded correctly and in accordance with the provisions. Although these roles cannot be dismissed as unimportant, they only constitute a minor portion of a much more extensive set of skills. Finance professionals are expected to make contributions toward strategy, contribute forward-looking information, and even have an impact on innovations in businesses. Technical prowess thus needs to be complemented by a hold on how the aspects of the finance factor fit in with marketing, operations, technology, and sustainability endeavors. In the new environment, constant education and thinking pro-actively are crucial to being competitive and relevant.
Mastering Technical Expertise in Modern Finance
Any career in finance is focused on technical knowledge. Finance professionals of the future have to be well versed in accounting principles, financial reporting standards that include IFRS and GAAP, corporate finance, taxation, and audit procedures. Nevertheless, the base is changing towards automation, artificial intelligence, and the cloud-based system capable of executing most of the traditional functions quicker and more precisely than before. Instead of eroding the role of finance experts, these tools will release more time to perform deeper work and value adding work.
A change-resistant finance professional knows how to prepare financial statements and therefore is not sufficient but should be able to interpret them to support rather strategic decisions. Financial modeling, scenario analysis, and valuation techniques are also becoming relevant and may be required more in those industries where making an investment decision is not easy and obviously at stake. Data analytics is gradually becoming a part and parcel of technical expertise as it allows finance professionals to draw useful insights out of massive datasets and convert them into usable insights.
What is more, regulatory compliance does not lie in one place. Attorneys, accountants, and others have to be aware of the evolution of accounting standards, tax regulations, and modifications in the industry-related regulations. As an example, the growing trends in sustainability reporting need compliances in the financial reporting with the environmental, social and governance (ESG) indicators. These necessities require technical precision as well as the capacity to present findings to a stakeholder who might not possess a financial degree. The skill to straddle the technical knowhow with good communication will be a differentiator.
Building Strategic and Business Acumen
Although technical skills are critically important, strategy ability is what gets a finance person out of the department into a managerial position. Strategic finance refers to being aware of the business environment, opportunity, and risks and toward long-term growth strategies. It is a process of trying to identify patterns behind the figures, market demands, forces, and competition at the time that would determine the future of the organizations.
Whether it be marketing, operations, or the top leadership, finance professionals who have good business acumen are able to work hand-in-hand with them to influence organizational strategy. They will also be able to determine how financially viable new products introduction or new market expansion or huge capital investments will be. Strategic decision-making is frequently linked to consideration of various events, trade-Offs between immediate returns forgotten about the customary inner preferences.
Such power of influence needs capacities to think on the basis of company mission and vision rather than quarterly targets. Knowledge of customer behavior and industry shakes as well as global economic conditions can play the role of creating context to make financial recommendations more applicable and convincing. With the combination of finance and strategic expertise, the contemporary finance expert actually becomes a business player, reinforcing innovation and survival in a competitive setting.

Leveraging Technology for Competitive Advantage
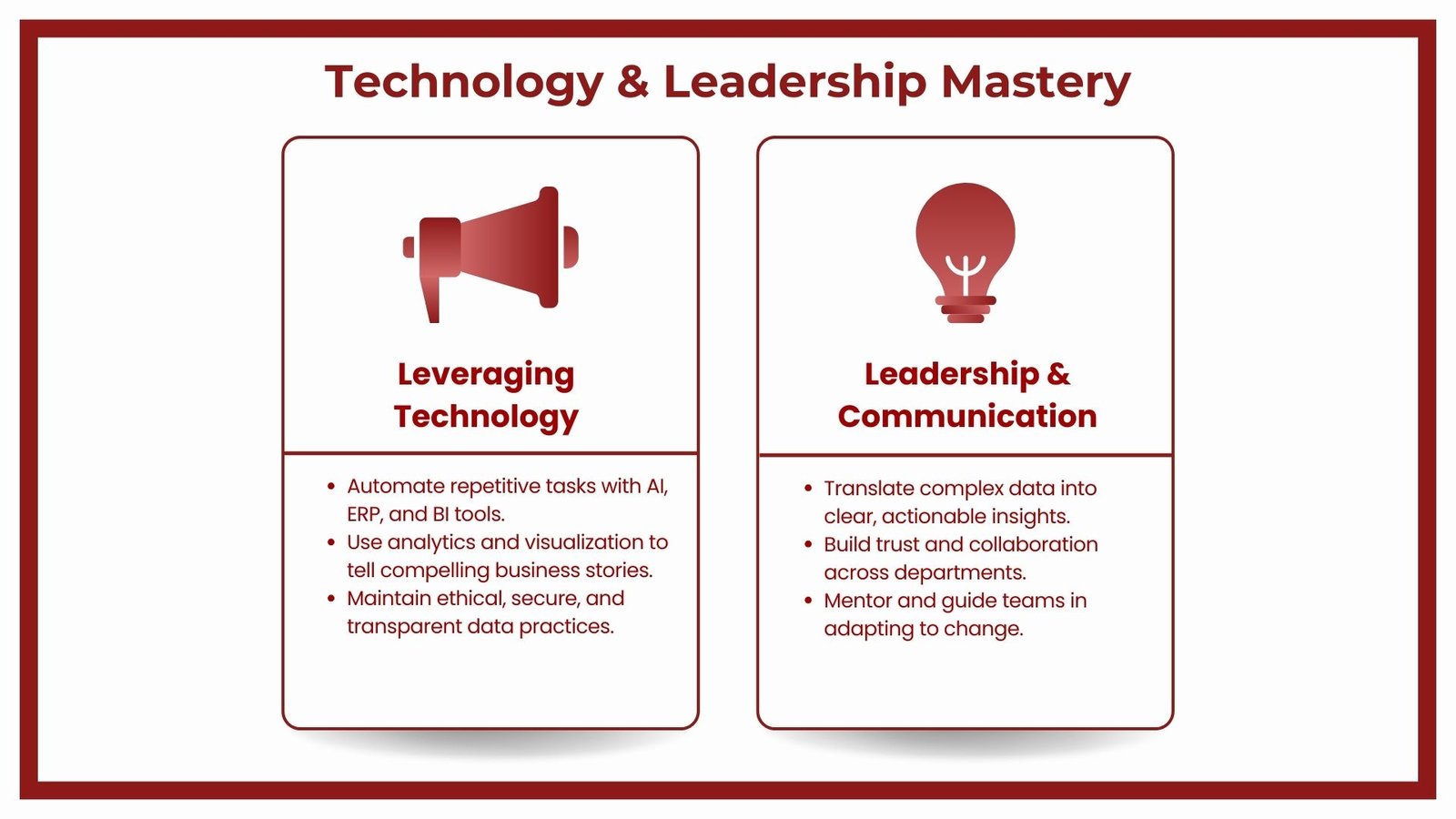
The finance profession has transformed in the fundamental way technology has come into play. Potential usage of the digital tools became a cornerstone of not only technical, but also strategic literacy. Automation reduces manual repetitive tasks like data entries, reconciliations and compliance checks and with advanced analytics and machine learning, there can be more precise forecasting and run risk models. The financial systems in the cloud are much friendlier since they make collaborative work and a more efficient reporting cycle possible so that the businesses base their decision process on the up-to-date information.
Digital literacy is a necessity to the aspiring future finance professional. These are enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, business intelligence master screens tools, and data visualization tools. The skills of data extraction, cleaning and interpretation can go a long way in ensuring speedy and accurate decision making. There is a competitive advantage to having professionals who have the ability to interpret the complex data into coherent business stories to the executives and potentially stakeholders of the businesses.
Nevertheless, the use of technology cannot only be considered using the newest tools; its use is also associated with the awareness of the limitations of technology as well as ethical aspects. Increasingly data privacy, cybersecurity and proper use of AI all come into play regarding their importance. Automations and analytics have to be carried out in a way that does not compromise the situation in regards to its integrity, transparency, and laws that must be adhered to by the finance professionals. The ability to mix technological fluency and good judgment in a quickly changing digital environment will be at a premium when new businesses apply technology in a rapidly changing digital environment.
Developing Leadership and Communication Skills
Leadership and communication are key skills as the finance professionals enter the world of more strategic roles. Finance communications are not all about delivering numbers even though it is mostly what is being delivered: the art of telling the story behind the numbers. Trends in modern management environments dictate that one clearly understands how to explain to non-financial managers, attend the board, negotiate with investors, etc. in accessible language given any complex concept put forward. Taking a professional leadership development course can help finance professionals strengthen these skills and apply them effectively in diverse business contexts.
Financial leadership is not confined to team managing either. It is the process of affecting the most effective decisions on the top management level, enhancing inter-departmental cooperation, and advancing a course which suits the long-term perspective of the organization. Emotional intelligence is a considerable phenomenon in this regard as it helps the professionals in the finance field to move around the dynamics prevalent at the work place, gain trust and handle conflicts.
Moreover, the leadership in the finance profession is composed of mentorship and knowledge exchange. When seasoned professionals invest in the growth of future talent, not only do they create more powerful organizations, but also improve their own reputation as sought after advisors and leaders. In a world that becomes more and more cross-functional in the world of finance, motivation and leadership of others is equally valuable to technical excellence.
Preparing for a Future-Ready Finance Career
Acquiring both technical and strategic expertise in the world of finance is not something that just happens overnight in order to become the future professional in the field. It entails an attitude of curiosity, changeability and ongoing learning. Remaining competitive in the field requires taking an active interest in avenues of increasing knowledge base–formal education, professional credentials, and experience at work. For many aspiring professionals, enrolling in a Career in financial modeling course Singapore provides a structured path to strengthen both technical and strategic skills. Changes, in terms of industry growth, technological advancements and modifications of the regulatory environment take place rather rapidly, therefore, professionals should take the initiative to change their skills.
Career-related networking is also one of the strong points of networking. Interaction with colleagues in the industry, attending finance conferences and joining professional associations can be a source of useful information about new trends and optimal practices. By developing a solid network of professionals, it is not only possible to open doors to a world of opportunities, but it will also provide a framework to overcome the challenges that are more nuanced.
Finally, the future financial professional is the one who can have accuracy and vision. They have to be careful in their technical details but fluid enough to change the strategies to changing business realities. Such innovators have to adopt technology without forgetting ethics. And as leaders they need to be ethical they should make sure the financial decisions they make are efficient both in short-term performance, and sufficiently to sustainability. Individuals who perfect this combination of technical and strategic skills will find themselves in a good position to succeed in a rapidly competitive and globally integrated economy