Complete Guide What Are Self Financed Courses for Professionals
Complete Guide What Are Self Financed Courses for Professionals
Understanding What Are Self-Financed Courses?
Self-finance courses refer to learning programs that are not subsidised by government funds or grants by institutions but rather it is through direct fees that are paid by learners themselves. This implies that the participants themselves foot the cost of running the course and the cost is not funded publicly or on a large institutional level. Such programs have become more popular in higher education, vocational training, and professional development, particularly in other countries where the university and colleges are exploring alternative sources of revenue to increase their programs and support levels of quality.
Self-financed courses may include full degree courses at universities, as well as short term certifications that may respond to industry needs. They tend to coexist with subsidized or government financed schemes, though they differ in their funding and, more often than not, their flexibility and concentration.
Even in the contemporary educational environment, the self-paid paths are occasionally perceived as an approach used by the institutions to respond fast to new competency requirements and market needs. The courses are not as sophisticated about strict requirements of public funding and as such can adjust to the changes in the industry necessities, advancements in technology, as well as global trends much faster.
They are also costlier to students because of the fact that they need full tuition fees thus they are a large drain on the financial resources of the students. It is important to know how these courses are conducted, the reason it is offered and the benefits or, otherwise, they bring to any student or professional contemplating it.
The Structure and Nature of Self-Financed Courses
The major difference between the self financed course is the source of its finance. In contrast to publicly funded programs whereby a fraction of expenditure is met by government budget, self established programs are self-repaying with the operational costs being paid by student fees and other related expenses. This expense would comprise of faculty wages, administrative resources, facilities utilization, lab supplies, library services and electronic resources. Tuition costs tend to be higher as compared to subsidized programs because institutions feel the need to make these programs self-sustaining in terms of finances.
There is a wide range of institutes offering self-financed courses, which includes government institutes, non-government institutions and some even include on-line training institutes. At the public institutions, these programs usually exist alongside the government-subsidized programs, although they are differentiated on the basis of charge structure, admission procedure and at times on faculty appointments also. Most or all courses in the private institutions can be based on a self-financed system since much of the running of the school is based on the fees paid by students with little or no government funding. Many of these programs are designed as comprehensive financial education courses in Singapore, helping learners gain practical knowledge and professional skills without relying on subsidies.
Self-financed courses may be more or less academically the same as established degree or diploma courses, or might be more flexible, in terms of both academic content and course design. An example of such integration is a self-funded master programme in data science that would facilitate the latest trends such as AI ethics or cloud computing at a much faster rate compared to publicly funded programmes, which may involve tedious approval procedures. Self-financed courses are specifically appealing to time-sensitive skills in the industries that focus on this.

Reasons Institutions Offer Self-Financed Courses
The emergence of the trend of self-financed courses has a number of strategic and financial reasons. A significant cause has been the growing pressure on schools to develop their own sources of income. As competition increases and funds supplied to higher education remain limited, universities and training institutions resort to self-financing course provision as a form of increasing their sources of revenue. This is supplemental revenue that can be used to renovate buildings, purchase new technology and recruit talented faculties.
Market responsiveness also contributes to another reason. Self-financed courses allow the institutions an opportunity to create specific programs without and without having to wait until the government approves the programs and gives funds to the programs. This may be especially useful when dealing with the rapidly shifting sphere, such as the digital marketing sector, renewable energy, or fintech, with its professional and technological advancements. With an initiative to introduce a self-financed program, a university will satisfy the current needs of the industry and get enrollees who wish to stay in the spotlight of the new trends.
Self-financed courses also enable institutions to focus on certain varieties of student groups like working professionals endeavoring in career upliftment or international students who can pay high fees to enroll in special training. Such flexibility in targeting the audience does not only increase the coverage of the institution; it leads to the creation of diversity (in the classroom), which may promote peer learning and networking in the course.
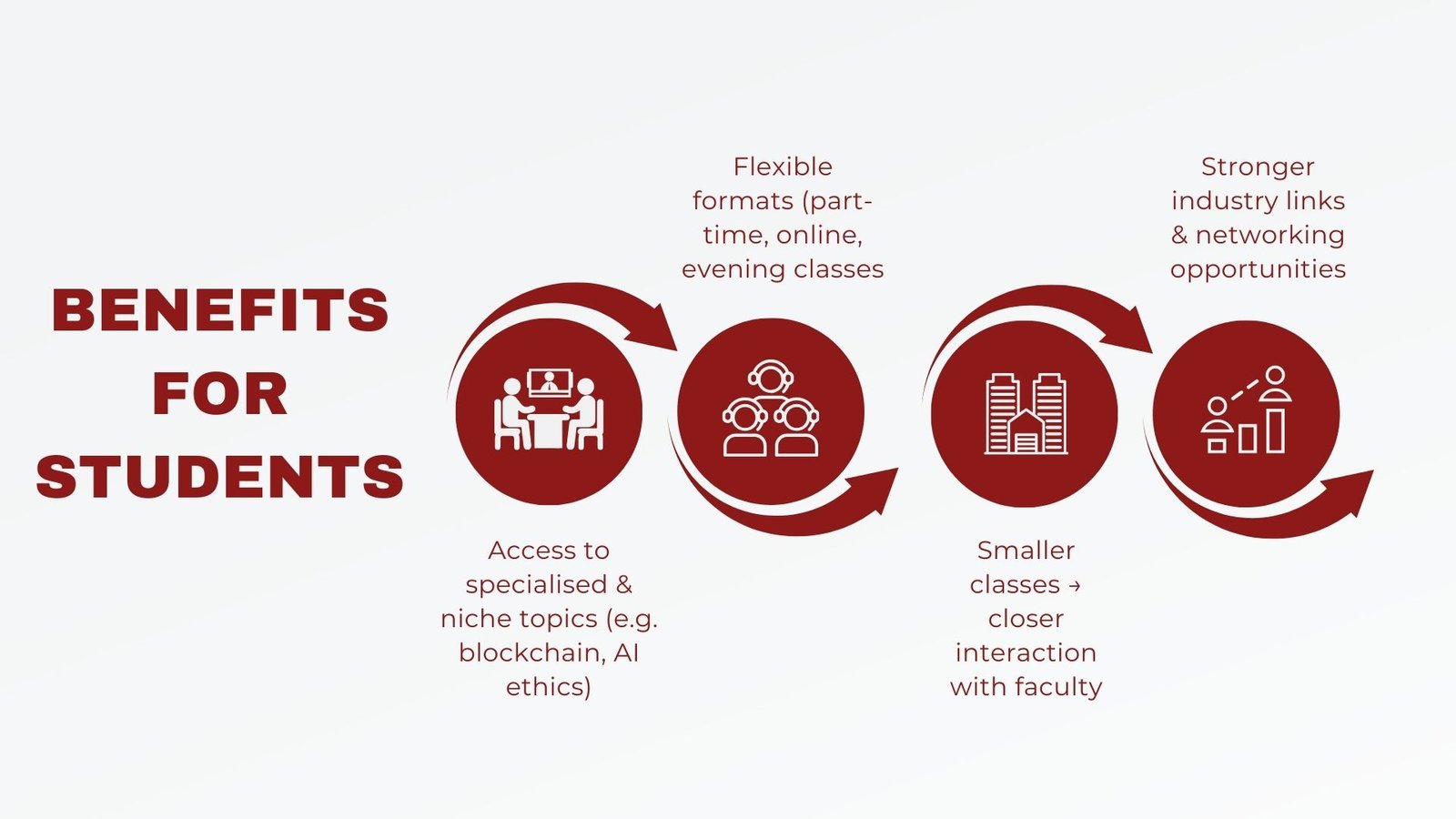
Benefits for Students
Self-financed courses may have various benefits to students, whereas they have considerably more expenses in most cases. Among the most important advantages is the possibility of niche and specialized topics which could not be offered in the conventional programs. As an example, a university could have a self funded postgraduate diploma on blockchain applications which is yet to be part of its usual subsidized course. These programs also enable learners to acquire knowledge in skills that closely match the trend in industries and positions.
The other advantage is flexibility of scheduling and format. A large number of self-financed modules are shaped to meet the part-time students, evening school, or internet contribution. This attributes to their suitability with working professionals who are unable to devote their time on campus studies. The self-funded program also leans to a more flexible curriculum offering guest lecturers, industry-based projects, real-world practical workshops that can be applied to academia studies.
In smaller classes as well as close and personal interaction with instructors, students in self financing courses can also be pleased with a more direct approach to instructors, especially in a professional course of studies. It can bring a more engaging learning and individually tailored support to academic life. In addition, since such programs usually work in close connection with the industry partners, the graduates stand a chance of having superior networking chances and being more consistent with their employer demands.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
As much as there are appealing benefits associated with self-financed courses, there are also challenges that potential students should consider. The first that comes around is the cost. Fees in self-funded courses could be significantly higher as compared to subsidized ones and this could leave the course unaffordable to a financially deprived student. The differentiating cost may be validated by the specific offerings and industry contacts made by the program but the student should consider whether the career prospects to be gained justify the financial load.
The other recommendation is recognition and credibility. Although numerous self-financed programs are very reputable, some of them can potentially lack institutional prestige or accreditation compared to their publicly funded counterparts. This may be especially significant in highly regulated occupations, where a particular degree is necessary to be licensed/certified. Students are advised to do research on whether a self funded course is attainable to the needed standards both in academics and industry related to the desired line of work.
Moreover, since self-financed courses are not government-aiding, it is possible to control the development of the custom and quality control even less. Although this may facilitate innovation, it may cause variation in the quality of programs. Before enrolling in schools, prospective students ought to analyze faculty qualifications, course syllabuses, and graduate products.

The Growing Role of Self-Financed Education in a Global Context
The market of non-loan driven courses is growing globally as a result of increased educational aspirations, dynamic changes in technology and corresponding transformation of labour market demands. These programs can be taken up as an option by the institutions in areas where government money may not be available to expand the system. In more developed education systems, self-funded education serves to plug the gaps where the mainstream educational systems fail to do so with special and career oriented education provided to niche markets.
Online learning has also increased the rampantness of self-financed education. Institutions can use digital platforms to make affordable, expandable courses that will appeal to any student around the globe. This has in turn yielded a more competitive market of self financed courses wherein providers focus on the academic quality as well as student experience, career services and alumni networks.
In the long run, the self-financed courses are prone to becoming a vital aspect in lifelong learning, where the professionals keep on updating their skills in order to stay competitive. Such programs may even begin to be indirectly sponsored by the government and policymakers who have realized that it is beneficial in developing the workforce.
Conclusion
Self-funded courses are important as they mark a change in the manner in which education is conducted as well as funded. These programs allow institutions the freedom to adapt to market requirements, introduce new content, and also reach a certain category of students through the use of tuition fees instead of being publicly subsidized. Self-financed courses may offer the individual learner access to special subjects, flexible forms of learning, and industry-oriented training.
For example, a hands-on advanced finance course in Singapore can give learners practical skills while aligning with market needs. However, this additional value usually comes at learning premiums, requiring careful evaluation of the quality of the course offered. Since the world will continue to require more flexible, vocationally-oriented education, it is quite possible that self-paid training programs will become an even stronger aspect of the educational system, defining the talents of the new generations and the possibilities they could use.